Neural Stem Cells
What are Neural Stem Cells?
Neural stem cells are a subtype of progenitor cells in the nervous system that can self-renew and give rise to differentiated lineages of neurons and glial cells, including oligodendrocytes and astrocytes.
Neural stem cells are present during neural development and in the adult brain. The stem cell niche architecture allows adult neural stem cells to continuously generate neurons in the brain throughout life. Adult neural stem cells are found mainly in two neurogenic regions: the hippocampus and the subventricular zone (SVZ), as well as in some non-neurogenic regions, such as the spinal cord.
Neural Stem Cells Inhibitors |
|
|---|---|
| Cat. No. | Product Name / Activity |
| 8913 | NVP-TNKS656 New |
| Used to generate neurons from epiblast stem cells; potent Tankyrase (AKA PARP5) inhibitor | |
Other |
|
| Cat. No. | Product Name / Activity |
| 2939 | A 83-01 |
| Promotes neural differentiation of hPSCs; selective inhibitor of TGF-βRI, ALK4 and ALK7 | |
| 7163 | Chroman 1 |
| Highly potent and selective ROCK 2 inhibitor; improves cell survival after cryogenesis | |
| 6476 | Compound E |
| Induces neuronal differentiation; γ-secretase inhibitor | |
| 2634 | DAPT |
| γ-secretase inhibitor; induces neuronal differentiation; blocks Notch signaling | |
| 1141 | Dibutyryl-cAMP, sodium salt |
| Promotes differentiation of hPSCs to dopaminergic neurons; cell-permeable cAMP analog | |
| 3093 | Dorsomorphin dihydrochloride |
| Promotes neural differentiation of hPSCs; also BMP type I receptor inhibitor | |
| 0927 | Fluoxetine hydrochloride |
| 5-HT reuptake inhibitor; induces differentiation of neuronal precursors | |
| 1099 | Forskolin |
| Adenylyl cyclase activator; induces neuronal differentiation | |
| 4912 | GsMTx4 |
| Neuroprotective compound; enhances neurogenesis in human neural stem cells | |
| 7807 | Hh-Ag1.5 |
| Promotes neural differentiation of hPSCs; potent and high affinity Smo receptor agonist | |
| 2845 | IBMX |
| PDE inhibitor; facilitates differentiation of neural progenitor cells | |
| 4439 | ISX 9 |
| Neurogenic agent; induces neuronal differentiation of SVZ progenitors and also induces cardiomyogenic differentiation | |
| 6053 | LDN 193189 dihydrochloride |
| Potent and selective ALK2 and ALK3 inhibitor; promotes neural induction of hPSCs | |
| 8150 | LDN 193189 in solution |
| Sterile-filtered 10 mM solution of LDN 193189 pre-dissolved in water | |
| 2864 | Metformin hydrochloride |
| Activator of LKB1/AMPK; enhances neurogenesis | |
| 6668 | ML 184 |
| Promotes NSC proliferation and differentiation; also selective GPR55 agonist | |
| 7874 | N-Acetylcysteine |
| Stimulate neuron differentiation and neuritogenesis of ESCs; also GSH precursor; antioxidant | |
| 3854 | 1-Oleoyl lysophosphatidic acid sodium salt |
| LPA1 and LPA2 agonist; inhibits differentiation of neural stem cells into neurons | |
| 3044 | PD 173074 |
| Selective FGFR1 and -3 inhibitor; inhibits proliferation and differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitors | |
| 3534 | PNU 74654 |
| Promotes neural differentiation of hPSCs; inhibits Wnt signaling | |
| 0695 | Retinoic acid |
| Promotes neural differentiation; endogenous retinoic acid receptor agonist | |
| 4366 | SAG |
| Enhances neuronal differentiation of iPSCs into dopaminergic neurons; Smo agonist | |
| 6390 | SAG dihydrochloride |
| Dihydrochloride salt of SAG; Smo receptor agonist | |
| 1614 | SB 431542 |
| Promotes neural differentiation of hPSCs; inhibitor of TGF-βRI, ALK4 and ALK7 | |
| 3300 | SU 5402 |
| Potent FGFR and VEGFR inhibitor; attenuates integrin β4-induced differentiation of neural stem cells | |
| 8093 | Tazemetostat |
| Induces neuronal differentiation genes; increases neurite extension. EZH2 inhibitor. | |
| 7405 | TWS 119 |
| Induces neuronal differentiation in ESCs; potent GSK3 inhibitor | |
| 1254 | Y-27632 dihydrochloride |
| Selective ROCK inhibitor; part of cocktail used to induce neurons from fibroblasts | |
| 7000 | Y-27632 in solution |
| Sterile-filtered 10 mM solution of Y-27632, selective ROCK inhibitor, pre-dissolved in water | |
Neural Stem Cells Differentiation
Neuronal differentiation is guided by key signaling pathways including Wnt, BMP, FGF and retinoic acid (RA) signaling cascades. The generation of neural progenitors is characterized by expression of neuroepithelial markers, such as nestin, PAX6, SOX1, SOX3, PSA-NCAM and MUSASHI-1 in vitro, and the formation of neural rosettes, reminiscent of neural tube initiation in vivo. Various methods have been developed for the conversion of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and embryonic stem cells (ESCs) into neuronal lineages, with a view to improving our understanding of neurological diseases and the neurobiological processes involved in development.

Figure 1. Generation of neurons from hiPSCs. From Qi et al. (2017) Nat.Biotechnol. 35 154. View our stem cells protocols for further information.
Noggin is an endogenous bone morphogenic protein (BMP) antagonist and a known neural-inducing factor. Chambers et al. (2009) reported that dual inhibition of SMAD signaling by Noggin, and the small molecule TGF-β antagonist, SB 431542 (Cat. No. 1614), promotes rapid and complete induction of PAX6+ neuroepithelial cells from hESCs capable of rosette formation. It has subsequently been found that the small molecule ALK2/3 antagonist LDN 193189 (Cat. No. 6053) can substitute Noggin in dual SMAD inhibition for the generation of neural progenitors (NPs). By exposure to small molecule activators of Hedgehog signaling, such as Purmorphamine (Cat. No. 4551), these NPs can be directed to become midbrain floor plate (FP) precursors, characterized by the expression of the marker FOXA2. Activation of Wnt signaling, using the potent GSK-3β inhibitor CHIR 99021 (Cat. No. 4423), promotes the conversion of these FP precursors to a dopamine (DA) neuron fate (Kriks et al., 2011), characterized by the co-expression of FOXA2 and the roof plate marker LMX1A, and in vivo studies showed robust survival and function of the engrafted midbrain DA neurons without neural overgrowth. Li et al. (2011) discovered that combined inhibition of GSK-3β, TGF-β and Notch signaling with CHIR 99021, SB 431542 and the γ-secretase inhibitor Compound E (Cat. No. 6476), respectively, rapidly converts monolayer cultured hESCs to homogenous primitive neuroepithelium within one week. This small molecule cocktail leads to the loss of the pluripotency markers, Oct4 and Nanog with a concurrent increase in PAX6 expression. Expression of Sox2, which is both a pluripotency marker and a marker of neural differentiation, remains unchanged.
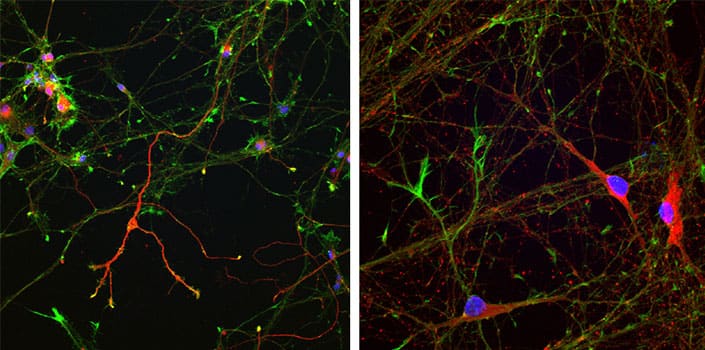
Figure 2. Dopaminergic neurons derived using SB 431542, CHIR 99021, DAPT and Purmorphamine. Cells cultured in Neuronal Media supplemented with TGFβ3 (Cat. No. 8420-B3, R&D Systems), cAMP, GDNF (Cat. No. 212-GD, R&D Systems), BDNF (Cat. No. 248-BDB, R&D Systems), N21-MAX (Cat. No. AR008, R&D Systems). Images courtesy of Kevin Flynn, Bio-Techne.
Cultured DA neurons have the potential to be used as cell therapy for Parkinson's disease (PD). Researchers at Kyoto University (Kikuchi et al., 2017) have generated DA neuron precursors from hiPSCs derived from healthy donors and patients with PD. Their method uses dual SMAD inhibition by LDN 193189 and the TGF-β inhibitor A 83-01 (Cat. No. 2939) for neuronal induction followed by induction of floor plate cells with Purmorphamine, CHIR 99021 and FGF-8. They have shown that dopaminergic progenitors derived in this way survive and function as midbrain DA neurons when transplanted into animal models of PD and that the recipients show increased spontaneous movement following transplantation. The method devised by Kikuchi et al. has been used in a clinical trial for Parkinson's disease at Kyoto University. In the context of stem cell therapy for regenerative medicine, PluriSln 1 (Cat. No. 4847) could be a useful tool as it selectively eliminates undifferentiated hPSCs from culture.
Qi et al. (2017) combined these approaches and devised a protocol using six small molecules for the rapid induction of early-born cortical neurons from hPSCs in 16 days. Their method uses dual SMAD inhibition with LSB, and DAPT (Cat. No. 2634) replaces Compound E as the γ-secretase inhibitor. The tankyrase inhibitor XAV 939 (Cat. No. 3748) is used to activate Wnt signaling in place of CHIR 99021 and additional inhibition of FGF signaling with SU 5402 (Cat. No. 3300) and PD 0325901 (Cat. No. 4192) was also used. Cells cultured in vitro exhibit functional electrophysiological properties by day 16, in the absence of glial cell co-culture. When transplanted into postnatal mouse cortex at day 8 of differentiation the resulting neurons establish long-distance connections (Figure 2).
Literature for Neural Stem Cells
Tocris offers the following scientific literature for Neural Stem Cells to showcase our products. We invite you to request* your copy today!
*Please note that Tocris will only send literature to established scientific business / institute addresses.
Huntington's Disease Research Product Guide
This product guide provides a background to Huntington's disease research and lists around 100 products for the study of:
- Somatic Instability
- Proteolysis and Inclusion Bodies
- Transcriptional Dysregulation
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction
- Nuclear-Cytoplasmic Transport Interference
- Excitotoxicity
- Stem Cells
Stem Cells Scientific Review
Written by Kirsty E. Clarke, Victoria B. Christie, Andy Whiting and Stefan A. Przyborski, this review provides an overview of the use of small molecules in the control of stem cell growth and differentiation. Key signaling pathways are highlighted, and the regulation of ES cell self-renewal and somatic cell reprogramming is discussed. Compounds available from Tocris are listed.
Huntington's Disease Poster
Huntington's disease (HD) is a severe monogenic neurodegenerative disorder, which is characterized by the prevalent loss of GABAergic medium spiny neurons (MSN) in the striatum. This poster summarizes the effects of mutant huntingtin aggregation implicated in the pathology of HD, as well as highlighting the use of iPSCs for HD modeling.
Parkinson's Disease Poster
Parkinson's disease (PD) causes chronic disability and is the second most common neurodegenerative condition. This poster outlines the neurobiology of the disease, as well as highlighting current therapeutic treatments for symptomatic PD, and emerging therapeutic strategies to delay PD onset and progression.
Stem Cell Workflow Poster
Stem cells have potential as a source of cells and tissues for research and treatment of disease. This poster summarizes some key protocols demonstrating the use of small molecules across the stem cell workflow, from reprogramming, through self-renewal, storage and differentiation to verification. Advantages of using small molecules are also highlighted.