Ribonucleotide Reductase
Ribonucleotide Reductases (RNRs) are iron-dependent reductase enzymes that catalyze the rate-limiting step of de novo deoxynucleotide (dNTP) synthesis. Ribonucleotide reductase is composed of two subunits; RNR1 and RNR2, which form heterodimeric tetramers.
Ribonucleotide Reductase Inhibitors |
|
|---|---|
| Cat. No. | Product Name / Activity |
| 3259 | Gemcitabine hydrochloride |
| Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor | |
Ribonucleotide Reductases (RNRs) are iron-dependent reductase enzymes that catalyze the rate-limiting step of de novo deoxynucleotide (dNTP) synthesis. There are three classes of RNRs (Classes I - III), but only class I are present in eukaryotes. Ribonucleotide reductase is composed of two subunits; RNR1 and RNR2, which form heterodimeric tetramers and a unique feature of note is the requirement of a free radical for catalytic activity.
RNRs are allosterically regulated by the relative concentrations of ATP:dATP. In addition, to ensure a balanced supply of nucleotides for DNA synthesis, RNR substrate specificity is modulated by ATP and GTP binding to the active site. Perturbations in RNR expression is a hallmark of malignant transformation and many cancer therapies target this enzyme.
External sources of pharmacological information for Ribonucleotide Reductase :
Literature for Ribonucleotide Reductase
Tocris offers the following scientific literature for Ribonucleotide Reductase to showcase our products. We invite you to request* your copy today!
*Please note that Tocris will only send literature to established scientific business / institute addresses.
Cancer Metabolism Research Product Guide
This product guide reviews some of the main areas in cancer metabolism research and lists around 150 products that can be used to investigate metabolic pathways in cancer including:
- Glycolysis
- Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
- Lipidogenesis
- 1C Metabolism and Nucleic Acid Synthesis
- Drivers of Metabolic Reprogramming
- pH and Redox Balance
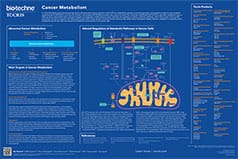
Cancer Metabolism Poster
This poster summarizes the main metabolic pathways in cancer cells and highlights potential targets for cancer therapeutics. Genetic changes and epigenetic modifications in cancer cells alter the regulation of cellular metabolic pathways providing potential cancer therapeutic targets.
Ribonucleotide Reductase Gene Data
| Gene | Species | Gene Symbol | Gene Accession No. | Protein Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RRM1 | Human | RRM1 | NM_001033 | P23921 |
| Mouse | Rrm1 | NM_009103 | P07742 | |
| Rat | Rrm1 | NM_001013236 | Q5U2Q5 | |
| RRM2 | Human | RRM2 | NM_001034 | Q96GD4 |
| Mouse | Rrm2 | NM_009104 | P11157 | |
| Rat | Rrm2 | NM_001025740 | Q4KLN6 | |
| RRM2B | Human | RRM2B | NM_015713 | Q9NTD8 |
| Mouse | Rrm2b | NM_199476 | Q6PEE3 | |
| Rat | Rrm2b | NM_001130543 | XP_235367 |