Rhobo6 ECM Dye User Guide
This is intended as a guide only; for full experimental details please read the reference provided.
In Brief Download the PDF of this protocol
This protocol is supplied by Antonio Fiore and Kayvon Pedram, HHMI's Janelia Research Campus and is to be used in combination with their publication: Live imaging of the extracellular matrix with a glycan-binding fluorophore. Nature Methods 22, 1070–1080 (2025).
1. Introduction
Rhobo6 ECM Dye is a cell impermeable small molecule fluorophore that labels extracellular matrix (ECM) components by reversibly binding glycans. This user guide provides instructions for Rhobo6 ECM Dye resuspension, storage, labeling, and imaging. The dye’s photophysical and biochemical properties, along with protocols for its use in various model organisms can be found in Fiore et al. (2025). All figure references in this guide correspond to figures in that manuscript.
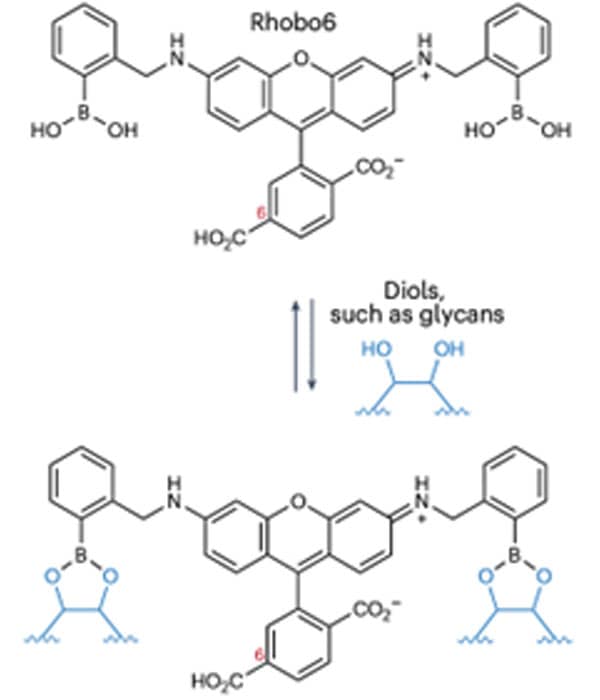
Figure 1: Rhobo6 ECM Dye structure and propensity for reversible glycan binding
2. Dye Handling, Storage and Resuspension
- Rhobo6 ECM Dye is provided as a 76 µg (100 nmol) lyophilized unit.
- It is shipped at ambient temperature and upon receipt, lyophilized vials should be stored at -20 °C.
- For in vitro experiments, users should resuspend the supplied Rhobo6 ECM Dye pellet directly in 100 µL of biology-grade DMSO to give a 1 mM stock solution at the time of using. For animal injections we advise resuspending into 10 µL of DMSO by pipetting any material off the walls of the test tube and being careful not to leave any residual material in the pipette tip. Next add 90 µL of PBS and pipette up and down until all material is in solution. Additionally, mix well by vortexing to ensuring the pellet has been fully resuspended.
- In some cases, the full 100 nmol aliquot is used for animal injection (see Section 5).
Otherwise, aliquoting is beneficial:
- Freeze 10 x 10 µL aliquots of 1 mM stock. Store aliquots at -80 °C, and discard after a maximum of 3 freeze-thaw cycles.
3. General Considerations
- Rhobo6 ECM Dye will accumulate intracellularly in cells that have compromised cell membranes, due for example to cell death or chemical fixation (cf. Extended Data Fig. 3d, 4d). This typically prevents ECM visualization. Rhobo6 should only be used with live samples or decellularized tissues.
- Rhobo6 ECM Dye cannot cross live cell membranes. Therefore, whole organisms typically cannot be labeled by bathing. In such cases, injections or incisions are required for dye delivery (cf. Extended Data Fig. 5c, 5e).
- Rhobo6 ECM Dye performs well with large, condensed ECM structures (e.g., tissue fascia, fiber bundles, thick mucin layers, etc.) and less well with loosely distributed or nanoscale ECM structures (e.g., spheroid basement membrane, cultured cell glycocalyx). Cf. Extended Data Fig. 3d, wild-type MCF10A.
- Rhobo6 ECM Dye labeling should be performed at a physiological pH of 7-7.5. Labeling is unlikely to work below pH 6 due to reduced boronic acid-diol affinity at low pH.
4. Protocol for Sample Bathing
- For bathing, the typical Rhobo6 ECM Dye working concentration is 5 µM, which can be achieved by diluting a 1 mM DMSO dye stock 1:200.
- The recommended incubation time is 1 h in the dark, under sample-specific incubation conditions. E.g., if a sample is normally grown at 37 °C with 5% CO2, use those conditions during Rhobo6 ECM Dye labeling.
- Rhobo6 ECM Dye labeling is fully reversible (cf. Extended Data Fig. 4d-e). Therefore, unless there is an intent to wash Rhobo6 ECM Dye away, Rhobo6 ECM Dye must remain in contact with the sample during imaging.
5. Protocol for Injection in Live Mice
- For administration to mice, retroorbital injection is recommended. Tail vein, intraperitoneal and subcutaneous injections have not yet been tested.
- Take the resuspended Rhobo6 ECM Dye prepared for animal injection in section 2. Centrifuge briefly to ensure absence of bubbles, then load entire volume into an insulin syringe.
- Anesthetize mouse, then inject retro-orbitally. Wait ~30 mins prior to live imaging. Rhobo6 ECM Dye will clear from the mouse’s system, and therefore imaging is best within a 4-hour window after initial injection.
- Animals can be imaged intravitally (cf. Fig. 5d-f) or euthanized for tissue and/or organ collection (cf. Fig. 4).
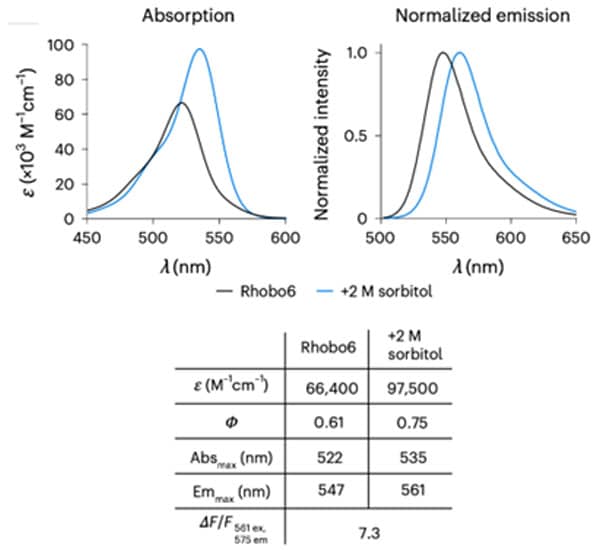
Figure 2. Top: Absorption and normalized emission spectra of Rhobo6 ECM Dye in unbound state (PBS) and bound state (PBS + 2 M sorbitol). Bottom: Photophysical properties of Rhobo6 ECM Dye .
6. Fluorescence Imaging with Rhobo6 ECM Dye
- Rhobo6 ECM Dye exhibits a fluorescence turn-on and redshift in both absorption and emission upon binding glycans. For optimal contrast use a 561 nm excitation laser with a 575 long-pass emission filter (cf. Extended Data Fig. 1e-h).
- These settings on commercial microscope systems might be similar to presets labeled as “RFP”, “mCherry” or “TexasRed”. We recommend checking your microscope preset to ensure optimal contrast and signal-to-background ratio.
- Due to replenishment from excess unbound dye, Rhobo6 ECM Dye signal is resistant to photobleaching (cf. Extended Data Fig. 3b-c).
7. Multiplexing Other Fluorescent Probes with Rhobo6 ECM Dye
- Unbound Rhobo6 ECM Dye can be excited by a 488 nm laser line (cf. Extended Data Fig. 1e-h). As a result, multiplexing with green fluorophores requires attention to the emission filters to minimize fluorescence crosstalk.
- For multiplexing with GFP, AF488, or similar, we recommend a cut-off wavelength of 525 nm for the green emission filter.
- For multiplexing with far red probes like AF647, Atto647N, or similar, we recommend setting the upper cutoff for Rhobo6 ECM Dye emission filter to 630 nm.
- If possible, we advise acquiring Rhobo6 ECM Dye and other fluorescent signal that may be spectrally close to it in separate temporal tracks, to minimize crosstalk signal.
8. Two-photon and STED Microscopy with Rhobo6 ECM Dye
- For 2P imaging, we recommend exciting Rhobo6 ECM Dye at 800 nm with a femtosecond laser. Emission filters should be kept at 575 nm long-pass as done for single photon fluorescence.
- For STED imaging, use a 660 nm depletion line.